The Ukraine war will no doubt follow Mr. Biden during stops in Seoul and Tokyo, hovering over his talks with the leaders.
Gestational Maternal Undernutrition: Implications on Fetal Development, Cardiovascular Diseases and Prevention by Complementary and Alternative Medicine
SUMMARY
There are reported links between sub-optimal maternal nutrition and compromised fetal development and growth leading to
higher cardiovascular disease (CVD) incidence in adolescence and later stages of life. CVDs are a major cause of disease and
death in mankind and are an impediment to sustainable human development, globally. Recent reports suggest that about 17.9
million human deaths are caused by CVDs, annually (WHO, 2022). Among the various CVDs, the most prevalent one is coronary
artery disease (CAD). The CAD resulted in about 9 million deaths and affected 110 million people, in 2015 (WHO, 2022). The
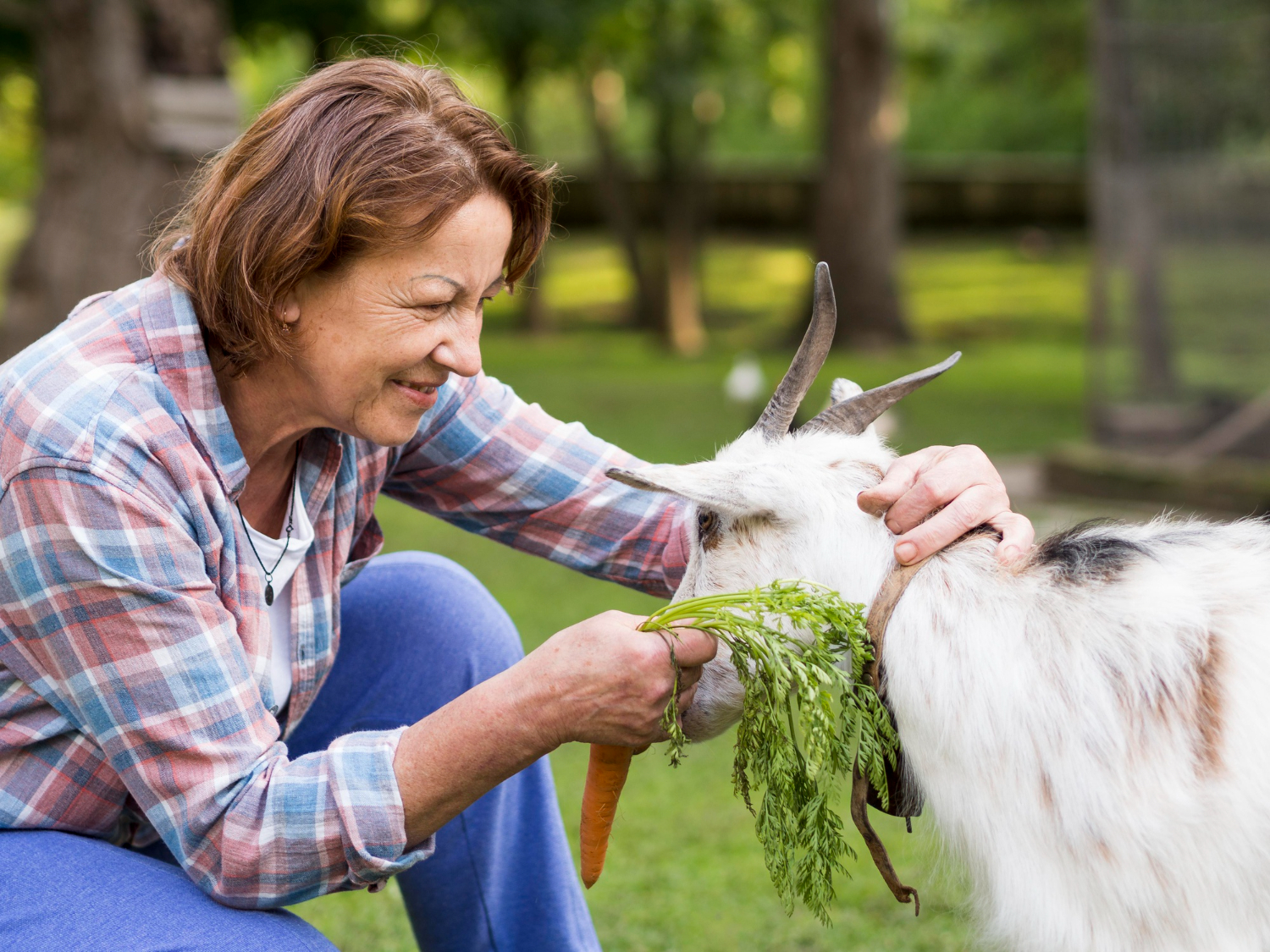
health of a woman and her generations depends upon nutritional status, during pregnancy and lactation. The risks of progressing
insulin resistance, high blood pressure, and type-2 diabetes mellitus in later stages of life were likely greater in babies born with
low birth weights than those born with normal weights and not exposed to maternal malnutrition. Complementary alternative
medicine (CAM) often includes the use of dietary supplements, such as specific vitamins and minerals, to support the nutritional
needs of both the mother and the developing fetus. Herbal sources of iron, such as nettle (Urtica dioica) and yellow dock (Rumex
crispus), have been historically used to address anemia and improve iron status. A positive impact of Moringa oleifera
supplementation has been demonstrated on maternal nutritional status and birth outcomes. Galactagogue herbs like fenugreek
(Trigonella foenum-graecum) and fennel (Foeniculum vulgare) have been traditionally used to enhance milk production and
support breastfeeding mothers.
- Department of Anatomy, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad-38040, Pakistan.
- Department of Pathology, University of Agriculture Faisalabad-38040, Pakistan.
- Corresponding author: drsarmadpk@uaf.edu.pk
INTRODUCTION
A wonderful serenity has taken possession of my entire soul, like these sweet mornings of spring which I enjoy with my whole heart. I am alone, and feel the charm of existence in this spot, which was created for the bliss of souls like mine. A wonderful serenity has taken possession of my entire soul.
I am so happy, my dear friend, so absorbed in the exquisite sense of mere tranquil existence, that I neglect my talents. I should be incapable of drawing a single stroke at the present moment; and yet I feel that I never was a greater artist than now was a greater.
The World Health Organization
IMPACT OF GESTATIONAL MATERNAL UNDERNUTRITION ON FETAL DEVELOPMENT
Maternal undernutrition has been proven to have a profound effect on fetal growth, with body weight and many key organs. It has been reported previously that during the first two weeks of pregnancy, the provision of a 5% protein diet only (undernutrition) led to a reduction in brain weight, size, and cortical thickness of the brain (Gressens et al., 1997). A severe gestational maternal protein restriction in rats caused a reduced number of glomeruli and hypertension in both male and female newborns, this hypertension is salt-sensitive and worsens with age, but is approximately equivalent in males and females (Woods et al., 2004)
Chronic energy deficit or maternal undernutrition means
having a body mass index (BMI) below 18.5. If the females are
under-nourished females at the time of conception, then during
pregnancy (when there are additional demands due to the
growing fetus), they are unlikely to improve their nutritional
status. They are more likely to fail to gain sufficient weight
during pregnancy and are at a higher risk of mortality than wellnourished and healthy women (Smith et al., 2003).
IUGR predisposes developing fetuses to reduced organ and
body weights. Most information about the long-term and short term effects of IUGR has come from animal models. In recent
years, many animal models of placental insufficiency and/or
poor maternal nutrition have been developed to investigate the
causes and effects of IUGR. Both maternal dietary
manipulations and surgical interventions have been employed
for these studies. A number of animal species have been studied
for IUGR effects, including rodents, rabbits sheep, and primates
(Louey et al., 2000; Mitchell et al., 2004; Jonker et al., 2018).


What to read next...
Sulaiman Khan, Riaz Hussain Pasha, Iqra Ali, Awais ur Rehman Sial, Ayesha Humayun, Adnan Hassan Tahir & Muhammad Arif Zafar
Hassnain Khan, Muzammil Zaman Khan, Mayra Ihsan, Nizam-Ud-Din1, Azka Zaheer, Bilal Ahmed Khan, Aneela Gul & Jameel Ahmed Buzdar
Evelyn Saba, Mansur Abdullah Sandhu, Arfan Yousaf, Usman Rashid & Man Hee Rhee